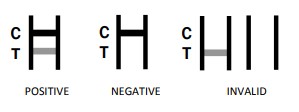First, nutrition Edible mushrooms need to absorb enough nutrients to grow and develop. Therefore, in the cultivation, in addition to using a suitable culture material, a small amount of sugar (glucose, sucrose 0.5 to 5%) and protein are added to the culture material. In addition, inorganic salts and vitamins are also essential nutrients for the growth and development of edible fungi. Generally, the medium is rich in content and does not need to be added. Second, the temperature The temperature range required for the growth of various edible fungi is different, and each edible fungus can only grow within a certain temperature range. According to the different requirements for temperature, edible fungi can be divided into three categories: Low temperature type: below 20 ° C, there are oyster mushrooms, mushrooms, mushrooms, mushrooms, Agaricus, etc.; Medium temperature type: 20~24°C, with golden mushroom, black fungus, white fungus, etc. High temperature type: 30 ° C or more, there are straw mushrooms and so on. Temperature is an important factor affecting the growth and development of edible fungi. If the temperature is too high or too low, it will affect the differentiation of fruiting bodies, resulting in reduced yield or no harvest. Third, moisture Moisture is an important component of edible fungi cells. Edible bacteria must have moderate moisture to grow normally, and most of the water needed for the growth and development of edible fungi comes from culture materials. For example, shiitake mushrooms require a wood pulp culture material with a water content of 55-60%, a segment wood of 35-40%, and a water content that cannot be too low or too high. Fourth, humidity Edible bacteria require different air relative humidity at different stages of development. During the growth of mycelium, the relative humidity of the air in the culture chamber is about 60%, and the period of fruit body formation should be about 90%. Five, air Edible fungi are aerobic fungi, and oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations are also important factors influencing the growth and development of edible fungi. Edible bacteria absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide through respiration. Therefore, the mushroom house should be kept well ventilated, with sufficient oxygen to avoid poor ventilation and high carbon dioxide concentration. Six, light According to the requirement of light in the formation period of the fruit body, the edible fungi can be generally divided into three types: light-emitting type, opto-optical type and intermediate type. Such as mushrooms, straw mushrooms, mushrooms and other edible fungi, do not form fruiting bodies under complete dark conditions, such edible fungi belong to the hi-light type, and its fruiting bodies can only grow well under the stimulation of scattered light. The optotype-type edible fungus does not require light stimulation throughout the life cycle. With light, the fruiting bodies cannot form or develop poorly, such as Agaricus bisporus, cockroaches, etc., and such edible fungi can grow under completely dark conditions. . The intermediate type edible fungus is not sensitive to light reaction, and its fruiting body can grow normally, with or without scattered light, such as yellow umbrella. Seven, pH Most edible fungi grow and develop like an acidic environment. The optimum pH value for mycelial growth is 5.0 to 5.3 on average. When the pH exceeds 8, the growth stops. Disclaimer: Some articles on this website are transferred from the Internet. If legal rights of third parties are involved, please inform this website. phone Hepatitis B Surface Antigen/AntibodyTest INTENDED USE
antigen in serum/plasma.
PRINCIPLE
If the test line does not appear, it is a negative result.
MAIN COMPONENTS
Sample pad, colloidal gold marked pad, nitrocellulose membrane, absorbent paper and PVC board.
INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
NEGATIVE: A red line appears in the control region(C). No line
INVALID: No red lines appear or control line fails to appear. Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test,Hepatitis B Test Kit,Medical Diagnostic Test Hepatitis B,Diagnostic Test Hbsag Changchun ZYF science and technology CO.,LTD , https://www.zyf-medical.com
Used for the qualitative detection of Hepatitis B surface
to combine with anti-mouse antibody and form a control line.
POSITIVE: Two distinct red lines appear. A red line in the
control region (C), and another red line in the test region (T). A pink to red line (T), even if it is very thin, indicates a positive
result.
appears in the test region (T).
Insufficient specimen volume or incorrect procedural
techniques are the most likely reasons. Review the procedure and repeat the test with a new test
device.
If the problem persists, discontinue using the kit and contact
your local distributor.