Anticancer effect of IL-18 with Armored CAR-T cell therapy
CAR-T therapy is one of the most promising treatments for cancer. Its anti-tumor effect is inseparable from the activity and expansion ability of T cells. In the previous issue, we have introduced that the addition of key cytokines will improve the efficacy of T cells. Overcoming the immunosuppressive microenvironment and improving the therapeutic effect of CAR-T therapy in liquid tumors and even solid tumors. Today we continue to introduce this cell therapy called "Armored CAR-T" (armor), and a new star molecule that boosts this CAR-T, the immunomodulator IL-18.
First, let's take a look at what is Armored CAR-T ?
Armored CAR-T: Armored is translated into armor, which gives the CAR-T cells a more powerful equipment. Specifically, it refers to the coexpression of some key cytokines or costimulatory ligands on the basis of the second/third generation CAR-T, namely the fourth generation CAR-T [1].
Significance: Whether it is hematoma or solid tumor, CAR-T cell activity is short, low proliferation, inhibition of tumor microenvironment will inhibit T cell activity, cytokine or co-stimulatory ligand can be added to immune regulation, significantly enhance T cells Amplification activity and longevity, icing on the cake.

Example: IL-12 : Systemic injection of IL-12 cytokines can cause severe inflammation, but after the fourth generation of CAR-T cells co-expressing IL-12 to achieve local expression, NK cells can be recruited at the tumor site, or directly Reversing the depleted tumor infiltrating T lymphocytes, effectively overcoming the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment and enhancing the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells and NK cells. As shown below, Armored CAR-T co-expressing IL-12 can improve CAR-T efficacy [1].
Since the current co-expression of cytokines is mostly, the narrow fourth-generation CAR-T, Armored CAR-T, can be understood as co-expressing cytokines, broadly expressing immunoregulatory factors, such as CD40L (CD40 ligand of TNFR family) and 4-1BBL (co-stimulatory ligands), which can additionally stimulate co-stimulation of antigen-presenting cells and enhance T cell activity [1]. The following figure shows the expression of 4-1BBL. The costimulatory receptor 4-1BB/4-1BBL promotes T cell proliferation, promotes DC cell activation and secretion of cytokines, and enhances cell lysis ability.

Therefore, the addition of cytokines (IL-7, IL-15, IL-18, IL-21, etc.) to the CAR-T design can promote the proliferation, activation and killing function of T cells. Following the previous issue, we have already understood the immune function of IL-7 . In this issue, we will introduce the function of cytokine IL- 18 and its relationship with tumor immunity.
IL-18 (interleukin-18, IL18) is an important immunoregulatory factor discovered in recent years, which can induce the proliferation and enhance the activity of immune cells. In recent years, its role in anti-tumor, anti-infection and immune regulation has been more It is widely studied, and these provide a theoretical basis and basis for the improvement of the effectiveness of CAR-T to break through the traditional limitations. Let's take a look at the immune function of IL-18.
First, the discovery of IL-18
IL-18 was discovered in 1995. It is called IFN-γ Inducing Factor (IGIF) because it induces IFN-γ production. It is also found to promote granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor ( The production of GM-CSF) and the reduction of IL-10 production were renamed IL-18 and belonged to the IL-1 family. Human and mouse IL-18 are mainly produced by macrophages, and various immune and non-immune cells such as monocytes, dendritic cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts can also be produced [2].
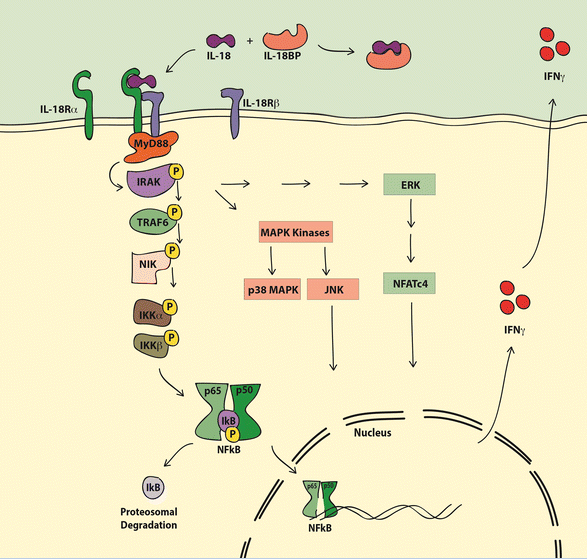
Second, IL-18 signaling pathway ( as shown below )
1 The IL-18 precursor present in the cell is processed and released to the extracellular;
2 mature IL-18 binds to the receptor complex IL-18Rα/IL-18Rβ;
3 Finally activates the NF-κB transcription factor, regulates gene transcription, and produces pro-inflammatory factors.
IL-18 regulates immune cell responses primarily by producing IFN-γ, which is dependent on IL-12 or IL-15, and studies have shown that IL-18 can induce IFN-γ in the presence of IL-12/15. When produced, and when they are not present, no trace or IFN-γ production is induced or induced [3].
Third, the function of IL-18 (as shown in the figure below [4])
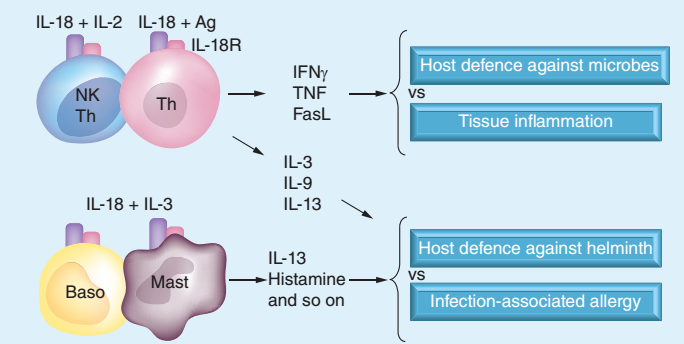
1. Regulation of T cells 1 Under the stimulation of IL-12, IL-18 can promote the proliferation of Th1 cells and secrete a large amount of IFN-γ, which can better eliminate antigens, especially intracellular bacteria, fungi and protozoa. ;
2 In the presence of some other stimuli, IL-18 can induce primitive or Th1-polarized cells to produce Th2 cytokines such as IL-13;
3 IL-18 also has an effect on Treg cells, and studies have shown that IL-18 can effectively inhibit the accumulation and function of Treg cells [5].
2. Regulation of NK cells 1 IL-18 stimulates the synthesis and secretion of IFN-γ in NK cells under the stimulation of IL-12;
2 IL-18 can increase the cytotoxicity of NK cells by increasing the expression of perforin, TNF and FASL;
3 For natural killer T cells (NKT cells), IL-18 can promote the synthesis of IFN-γ by natural killer T cells under the synergistic effect of IL-12. Under the stimulation of TCR, IL-18 can enhance the production of IL by NKT cells. 4. IL-5, IL-13, GM-CSF, TNF [6].
In addition, basophils and mast cells can also produce a large amount of IL-13 under the stimulation of IL-18, releasing chemical regulators such as histamine to protect the body from external pathogens.
Fourth, the anti-tumor effect of IL-18

Micallef After intraperitoneal injection of Meth A sarcoma cells in BALB/c mice, intraperitoneal injection or intravenous injection of IL-18 showed significant anti-tumor effects. The mice were pretreated with 1 μg of IL-18 3 h and 6 h before inoculation of the tumor cells, and the mice inoculated with the tumor survived, while the control mice died within 3 weeks. In vitro tests have shown that IL-18 itself has no anti-tumor effect, so its anti-tumor effect should be indirectly exerted by inducing NK cells and cytotoxic cells in mice. The following figure shows the effect of IL-18 treatment on NK cell activity [7].
How does the IL-18 anti-tumor mechanism occur?
1 First activate NK cells and secrete a large amount of IFN-γ to specifically kill tumor cells;
2 Under the regulation of NK cells, CD8 + T and CD4 + T cells gradually activate, CTL plays a killing effect, and CD4 + T cells participate in the formation of tumor-specific immune memory;
3 Anti-tumor effects can also be enhanced by activating cytokines produced by Th cells, such as secreted IL-2, which enhances killing activity by activating monocytes and macrophages.
V. Application of IL-18 in tumor immunotherapy <br> The above, the powerful function of IL-18 in immune regulation, its application in tumor immunity has been widely studied, compared with other cytokines, IL -18 showed a stronger anti-tumor effect with lower toxic side effects. It mainly includes the following aspects:
Application 1: A clinical phase I study of renal clear cell carcinoma [8], patients were given different doses of rhIL-18 (recombinant human IL-18), and the results showed that all patients were well tolerated, which also prompted patients The tolerance to IL-18 is 10-1000 times higher than that of IL-12 or IL-2, reflecting its low-level excellent properties.
Application 2: Tumor cells transfected with IL-18 gene have decreased tumorigenicity and prolonged survival of animals, indicating that IL-18 is a new anti-tumor factor, providing a new safe and effective clinical tumor treatment. s method.
Application 3: Tomura et al [9] studied the effect of IL-18 on NK cells in vitro. IL-18 alone was co-cultured with NK cells, and only a small amount of IFN-γ was produced, in the presence of IL-12 or IL-2. , can produce a large amount of IFN-γ. However, the combination of IL-18 and IL-12 has strong toxic and side effects, which can reduce the body weight of the tumor-bearing mice, mucosal erosion, diarrhea and the like. Experiments suggest that this side effect may be caused by IL-18. Therefore, it is also an important research direction to clarify the combination of various factors and dose adjustment.
In summary, IL-18, as an immunoregulatory factor, induces the secretion of IFN-γ, which significantly enhances the Th1-type immune response. Therefore, if the cytokine IL-18 is added to CAR-T, it is likely to enhance CAR- The efficacy of T can also reduce the amount of CAR-T cells used and the side effects of systemic administration. On the other hand, the enhancement effect of IL-18 on NK cells also provides new ideas and targets for our future CAR-NK. This issue is here first, let us look forward to the magical effect of IL-18 in CAR-T treatment! We will see you next time~
references
1. Yeku OO, Brentjens R J. Armored CAR T-cells: utilizing cytokines and pro-inflammatory ligands to enhance CAR T-cell anti-tumour efficacy[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2016, 44(2): 412-418 .
2. Wawrocki, S., et al., Interleukin 18 (IL-18) as a target for immune intervention. Acta Biochim Pol, 2016. 63(1): p. 59-63.
3. Sedimbi, SK, T. Hagglof, and MC Karlsson, IL-18 in inflammatory and autoimmune disease. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2013. 70(24): p. 4795-808.
4. Tsutsui H, Nakanishi K. Immunotherapeutic applications of IL-18 [J]. Immunotherapy, 2012, 4(12): 1883-1894.
5. Carroll, RG, et al., Distinct effects of IL-18 on the engraftment and function of human effector CD8 T cells and regulatory T cells. PLoS One, 2008. 3(9): p. e3289.
6. Uchida, T., et al., IL-18 time-dependently modulates Th1/Th2 cytokine production by ligand-activated NKT cells. Eur J Immunol, 2007. 37(4): p. 966-77.
7. Micallef, MJ, et al., Interleukin 18 induces the sequential activation of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes to protect syngeneic mice from transplantation with Meth A sarcoma. Cancer Res, 1997. 57(20): p. 4557-63 .
8. Robertson, MJ, et al., A dose-escalation study of recombinant human interleukin-18 using two different schedules of administration in patients with cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2008. 14(11): p. 3462-9.
9. Tomura, M., et al., A critical role for IL-18 in the proliferation and activation of NK1.1+ CD3-cell. J Immunol, 1998. 160(10): p. 4738-46.
First, let's take a look at what is Armored CAR-T ?
Armored CAR-T: Armored is translated into armor, which gives the CAR-T cells a more powerful equipment. Specifically, it refers to the coexpression of some key cytokines or costimulatory ligands on the basis of the second/third generation CAR-T, namely the fourth generation CAR-T [1].
Significance: Whether it is hematoma or solid tumor, CAR-T cell activity is short, low proliferation, inhibition of tumor microenvironment will inhibit T cell activity, cytokine or co-stimulatory ligand can be added to immune regulation, significantly enhance T cells Amplification activity and longevity, icing on the cake.

Example: IL-12 : Systemic injection of IL-12 cytokines can cause severe inflammation, but after the fourth generation of CAR-T cells co-expressing IL-12 to achieve local expression, NK cells can be recruited at the tumor site, or directly Reversing the depleted tumor infiltrating T lymphocytes, effectively overcoming the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment and enhancing the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells and NK cells. As shown below, Armored CAR-T co-expressing IL-12 can improve CAR-T efficacy [1].
Since the current co-expression of cytokines is mostly, the narrow fourth-generation CAR-T, Armored CAR-T, can be understood as co-expressing cytokines, broadly expressing immunoregulatory factors, such as CD40L (CD40 ligand of TNFR family) and 4-1BBL (co-stimulatory ligands), which can additionally stimulate co-stimulation of antigen-presenting cells and enhance T cell activity [1]. The following figure shows the expression of 4-1BBL. The costimulatory receptor 4-1BB/4-1BBL promotes T cell proliferation, promotes DC cell activation and secretion of cytokines, and enhances cell lysis ability.

Therefore, the addition of cytokines (IL-7, IL-15, IL-18, IL-21, etc.) to the CAR-T design can promote the proliferation, activation and killing function of T cells. Following the previous issue, we have already understood the immune function of IL-7 . In this issue, we will introduce the function of cytokine IL- 18 and its relationship with tumor immunity.
IL-18 (interleukin-18, IL18) is an important immunoregulatory factor discovered in recent years, which can induce the proliferation and enhance the activity of immune cells. In recent years, its role in anti-tumor, anti-infection and immune regulation has been more It is widely studied, and these provide a theoretical basis and basis for the improvement of the effectiveness of CAR-T to break through the traditional limitations. Let's take a look at the immune function of IL-18.
First, the discovery of IL-18
IL-18 was discovered in 1995. It is called IFN-γ Inducing Factor (IGIF) because it induces IFN-γ production. It is also found to promote granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor ( The production of GM-CSF) and the reduction of IL-10 production were renamed IL-18 and belonged to the IL-1 family. Human and mouse IL-18 are mainly produced by macrophages, and various immune and non-immune cells such as monocytes, dendritic cells, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts can also be produced [2].
Second, IL-18 signaling pathway ( as shown below )
1 The IL-18 precursor present in the cell is processed and released to the extracellular;
2 mature IL-18 binds to the receptor complex IL-18Rα/IL-18Rβ;
3 Finally activates the NF-κB transcription factor, regulates gene transcription, and produces pro-inflammatory factors.
IL-18 regulates immune cell responses primarily by producing IFN-γ, which is dependent on IL-12 or IL-15, and studies have shown that IL-18 can induce IFN-γ in the presence of IL-12/15. When produced, and when they are not present, no trace or IFN-γ production is induced or induced [3].

Third, the function of IL-18 (as shown in the figure below [4])

1. Regulation of T cells 1 Under the stimulation of IL-12, IL-18 can promote the proliferation of Th1 cells and secrete a large amount of IFN-γ, which can better eliminate antigens, especially intracellular bacteria, fungi and protozoa. ;
2 In the presence of some other stimuli, IL-18 can induce primitive or Th1-polarized cells to produce Th2 cytokines such as IL-13;
3 IL-18 also has an effect on Treg cells, and studies have shown that IL-18 can effectively inhibit the accumulation and function of Treg cells [5].
2. Regulation of NK cells 1 IL-18 stimulates the synthesis and secretion of IFN-γ in NK cells under the stimulation of IL-12;
2 IL-18 can increase the cytotoxicity of NK cells by increasing the expression of perforin, TNF and FASL;
3 For natural killer T cells (NKT cells), IL-18 can promote the synthesis of IFN-γ by natural killer T cells under the synergistic effect of IL-12. Under the stimulation of TCR, IL-18 can enhance the production of IL by NKT cells. 4. IL-5, IL-13, GM-CSF, TNF [6].
In addition, basophils and mast cells can also produce a large amount of IL-13 under the stimulation of IL-18, releasing chemical regulators such as histamine to protect the body from external pathogens.
Fourth, the anti-tumor effect of IL-18

Micallef After intraperitoneal injection of Meth A sarcoma cells in BALB/c mice, intraperitoneal injection or intravenous injection of IL-18 showed significant anti-tumor effects. The mice were pretreated with 1 μg of IL-18 3 h and 6 h before inoculation of the tumor cells, and the mice inoculated with the tumor survived, while the control mice died within 3 weeks. In vitro tests have shown that IL-18 itself has no anti-tumor effect, so its anti-tumor effect should be indirectly exerted by inducing NK cells and cytotoxic cells in mice. The following figure shows the effect of IL-18 treatment on NK cell activity [7].
How does the IL-18 anti-tumor mechanism occur?
1 First activate NK cells and secrete a large amount of IFN-γ to specifically kill tumor cells;
2 Under the regulation of NK cells, CD8 + T and CD4 + T cells gradually activate, CTL plays a killing effect, and CD4 + T cells participate in the formation of tumor-specific immune memory;
3 Anti-tumor effects can also be enhanced by activating cytokines produced by Th cells, such as secreted IL-2, which enhances killing activity by activating monocytes and macrophages.
V. Application of IL-18 in tumor immunotherapy <br> The above, the powerful function of IL-18 in immune regulation, its application in tumor immunity has been widely studied, compared with other cytokines, IL -18 showed a stronger anti-tumor effect with lower toxic side effects. It mainly includes the following aspects:
Application 1: A clinical phase I study of renal clear cell carcinoma [8], patients were given different doses of rhIL-18 (recombinant human IL-18), and the results showed that all patients were well tolerated, which also prompted patients The tolerance to IL-18 is 10-1000 times higher than that of IL-12 or IL-2, reflecting its low-level excellent properties.
Application 2: Tumor cells transfected with IL-18 gene have decreased tumorigenicity and prolonged survival of animals, indicating that IL-18 is a new anti-tumor factor, providing a new safe and effective clinical tumor treatment. s method.
Application 3: Tomura et al [9] studied the effect of IL-18 on NK cells in vitro. IL-18 alone was co-cultured with NK cells, and only a small amount of IFN-γ was produced, in the presence of IL-12 or IL-2. , can produce a large amount of IFN-γ. However, the combination of IL-18 and IL-12 has strong toxic and side effects, which can reduce the body weight of the tumor-bearing mice, mucosal erosion, diarrhea and the like. Experiments suggest that this side effect may be caused by IL-18. Therefore, it is also an important research direction to clarify the combination of various factors and dose adjustment.
In summary, IL-18, as an immunoregulatory factor, induces the secretion of IFN-γ, which significantly enhances the Th1-type immune response. Therefore, if the cytokine IL-18 is added to CAR-T, it is likely to enhance CAR- The efficacy of T can also reduce the amount of CAR-T cells used and the side effects of systemic administration. On the other hand, the enhancement effect of IL-18 on NK cells also provides new ideas and targets for our future CAR-NK. This issue is here first, let us look forward to the magical effect of IL-18 in CAR-T treatment! We will see you next time~
references
1. Yeku OO, Brentjens R J. Armored CAR T-cells: utilizing cytokines and pro-inflammatory ligands to enhance CAR T-cell anti-tumour efficacy[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions, 2016, 44(2): 412-418 .
2. Wawrocki, S., et al., Interleukin 18 (IL-18) as a target for immune intervention. Acta Biochim Pol, 2016. 63(1): p. 59-63.
3. Sedimbi, SK, T. Hagglof, and MC Karlsson, IL-18 in inflammatory and autoimmune disease. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2013. 70(24): p. 4795-808.
4. Tsutsui H, Nakanishi K. Immunotherapeutic applications of IL-18 [J]. Immunotherapy, 2012, 4(12): 1883-1894.
5. Carroll, RG, et al., Distinct effects of IL-18 on the engraftment and function of human effector CD8 T cells and regulatory T cells. PLoS One, 2008. 3(9): p. e3289.
6. Uchida, T., et al., IL-18 time-dependently modulates Th1/Th2 cytokine production by ligand-activated NKT cells. Eur J Immunol, 2007. 37(4): p. 966-77.
7. Micallef, MJ, et al., Interleukin 18 induces the sequential activation of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes to protect syngeneic mice from transplantation with Meth A sarcoma. Cancer Res, 1997. 57(20): p. 4557-63 .
8. Robertson, MJ, et al., A dose-escalation study of recombinant human interleukin-18 using two different schedules of administration in patients with cancer. Clin Cancer Res, 2008. 14(11): p. 3462-9.
9. Tomura, M., et al., A critical role for IL-18 in the proliferation and activation of NK1.1+ CD3-cell. J Immunol, 1998. 160(10): p. 4738-46.
Organic Garlic powder is processed, packed, and shipped hygienically without pesticide residue, additive, and preservatives. Our garlic powder products are of strong garlic taste, good color, lower SO2 content, and low bacterial. Organic Garlic powder is a very common seasoning. The spice is a highly nutritious vegetable with very few calories, containing trace amounts of other nutrients that contribute to its universal status of a powerful, beneficial healer. The natural medicinal ingredient, both as a fresh plant and supplement, can strengthen immune function and boost overall well-being.
Garlic Powder,Nutritious Vegetable,Garlic Powder Organic,Organic Garlic Powder
Organicway (xi'an) Food Ingredients Inc. , https://www.organicwayince.com