Release date: 2010-08-19 "Carbon nanotube" (carbon nanotube) is a carbon molecular material composed of tubular coaxial nanotubes accidentally discovered by researchers of NEC Corporation of Japan in 1991 when observing spherical carbon molecules produced by graphite arc equipment using an electron microscope. Carbon nanotubes are classified into single-layer carbon tubes and multi-layer carbon tubes. Studies have shown that carbon nanotubes have superior tensile strength, fatigue resistance and good electrical conductivity. In recent years, the developed countries led by the United States have conducted extensive exploratory research on the industrial application of carbon nanotubes as a new material, and found that it has a good application prospect in the field of medical devices. Source: Xinhuanet
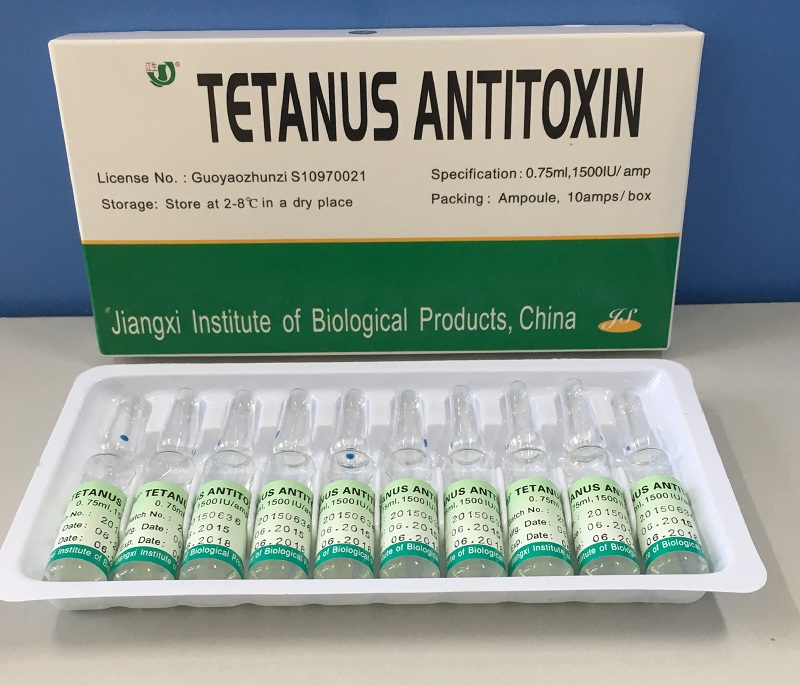
The main ingredient of Tetanus Antitoxin is that horse tetanus immunboglobulin following pepsin digestion. It's used for the prophylaxsis and therapy of tetanus.
The ATS Injection (equine origin) is efficient and affordable for patients, which maket share covers over 70% of China, and it's expored to over 20 countries, especially to Afica, southeast Asia, South Asia. We offer an array of Tetanus Antitoxin Injection in different strength, there are 1500IU, 3000IU, 5000IU, 10000IU.
Antitoxin Formulations For Human Antitoxin Formulations For Human,Tetanus Antitoxin,Tetanus Antitoxin Formulations,Antitoxin Formulations Essential Drug Jiangxi Institute of Biological Products Inc. , https://www.jxinstitute.com
The use of carbon nanotube permanent prostheses (such as prostheses, dentures, etc.) has become quite common. However, most prostheses can only be used for 10 to 15 years. Thereafter, the patient has to undergo a second surgery to replace the prosthesis. Two doctors from the National Institute of Medical Technology of Spain have developed a new series of prostheses with zirconium dioxide as the substrate and coated with carbon nanotubes, including artificial knee joints, artificial hip joints, dentures, etc. Up to 150 years. That is, once the prosthesis is implanted, the patient does not need to be replaced again.
Zirconium dioxide is a major component of many artificial ceramic materials, and its disadvantage is that it is easily worn. Spanish scientists use special spraying technology to spray carbon nanotubes on the surface of bioceramic prosthesis, which is equivalent to wearing a wear-resistant "tightsuit".
Carbon Nanotube Biosensors Currently, research institutes in many countries around the world are actively developing new biosensors that can quickly detect the presence of tumor cells in the body. A biosensor is coated with a layer of carbon nanotubes that adsorbs cancer-specific antibodies in advance, dropping a drop of blood from the patient onto the biosensor, and the cancer cells react rapidly with the antibody. The doctor can observe this reaction through a special optical instrument to determine if there are cancer cells and cancer cells in the patient. This new carbon nanotube biosensor is extremely sensitive and can diagnose a variety of early cancers.
Carbon Nanotube Wire Mesh Material The Advanced Materials Research Institute of Michigan State University has developed a new material for neutral carbon nanotube wire mesh. Such a mesh material can connect an integrated circuit or the like to a nerve cell, and can be used for controlling pain, for example, in patients with advanced cancer, burns, and serious car accidents, and severe pain patients who are difficult to use with conventional analgesics.
Researchers say that using carbon nanotube screens can not only make implantable devices and electronic painkillers, but even detect very weak currents from nerve cells, so using this new material can also produce seizure control and muscle contraction. Some of the new electronic medical device products, such as treatment equipment for elderly women with urinary incontinence and Parkinson's disease.
Carbon Nanotube Coated Implantable Electrodes The use of electrical pulse signals from implantable electrodes can treat a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders such as depression, Parkinson's disease, and epilepsy. However, the existing implanted electrodes are mostly metal products, and their working life is short. In order to overcome this technical problem, researchers at Texas State University conducted in-depth research. They found that the working life of the implanted electrode was significantly extended after the surface of the implanted electrode was coated with a layer of carbon nanotube material. The newly developed carbon nanotube coated electrode implanted experiments on primates have achieved satisfactory results.
Special nozzles for carbon nanotube coatings A large number of studies by American scientists have found that various implantable or surgical medical device products (such as vascular stents, catheters, microcapsules, pacemakers, endoscopes, etc.) are available on the market. The surface of heart valves, blood glucose detectors, sensors, medical textiles, blood vessels/vasters, orthopedic instruments, prostheses or prostheses, diagnostic equipment, etc., coated with a thin layer of carbon nanotube outer membrane can greatly improve their Work performance and make it better compatible with human tissue. However, this is technically difficult. However, Sono-Tek's Ultrasonics Inc. of the United States recently developed a new type of nozzle "Accumist". This product can spray carbon nanotube material on the surface of a variety of implantable or surgical instruments in an instant, and the coating is very strong and not easy to fall off. It reduces the amount of carbon nanotube material by 80% compared to conventional spray technology. This special nozzle for carbon nanotube coating film is also the world's first low-pressure ultrasonic atomic single-layer nozzle, which has been put into mass production.
Multifunctional Nano Carbon Pipeline The Carbon Nanotube Laboratory at the University of Cincinnati is well known in the materials science community. The lab uses special technology to spin carbon nanotubes into wires. This carbon pipeline has a wide range of uses in military communications and civilian products.
According to reports, the nanocarbon pipeline developed by researchers at the University of Cincinnati is only 25 microns in diameter, which is almost invisible to the naked eye. It can be processed into a degradable implantable medical device product, thus changing the existing implantable device product. After the surgery must be taken out of trouble.
Technology Extension Carbon Nanotubes A "double-edged sword"
Although carbon nanotubes are regarded as a new material in the 21st century by European and American developed countries, some Western countries' health departments have also put forward different opinions. The carbon nanotubes are very slender and difficult to identify with the naked eye. Experiments show that once it is Inadvertently inhaled into the lungs and reached a certain level, it will induce malignant tumors such as lung cancer and stromal cell tumor like asbestos fibers.
According to a report published in the 2008 issue of Natural Carbon Nanotubes by researchers at the University of Edinburgh in the United Kingdom, experiments have confirmed that mice eventually develop symptoms of stromal cell tumors after inhaling a certain amount of carbon nanotube gas.
Japan, the world's first to discover new carbon nanotube materials, recently issued the same warning. Officials from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare have warned Japanese researchers to pay attention to indoor ventilation during the carbon nanotube experiment to prevent large inhalation of carbon nanotubes. It can be seen that although carbon nanotubes are a new material with bright prospects and wide application, it is also a “double-edged swordâ€. How to prevent its potential harm to the human body remains to be explored by scientists.