In the fields of “ medical †and “labor employmentâ€, the depth of AI is more extensive, and the problems that can be brought about are more prominent and obvious in these two fields. "AI fairness" and "AI morality" are issues that everyone will pay attention to in the future: Will AI help the world's Datong or increase social injustice? And how to ensure that the benefits of AI are enjoyed by all humans? Part one: The current four key questions about artificial intelligence We will now delve into the current four key issues of artificial intelligence to provide readers with an opportunity to understand industry experts' insights and recommendations. Relevant discussions include the challenges, opportunities, and interventions available for each key issue. Social injustice How do artificial intelligence systems cause social injustices such as prejudice and discrimination? The role of artificial intelligence systems in the field of high-risk decision making is increasingly important – from credit, insurance to third-party decision making and parole issues. Artificial intelligence technology will replace the manual to decide who will get an important opportunity, and who will be abandoned, which will lead to a series of issues concerning rights, freedom and social justice. Some people think that the application of artificial intelligence systems can help overcome a series of problems caused by human subjective bias, while others worry that artificial intelligence systems will amplify these prejudices, but will further expand the unequal opportunities. In this discussion, the data will play a vital role and cause strong concern. The operation of artificial intelligence systems often depends on the data they receive and is a direct reflection of these data. It also includes the source of these data and the bias in the collection process. In this respect, the impact of artificial intelligence is closely related to the corresponding big data technology. In a broad sense, there are two forms of data bias. The first is that the collected data cannot objectively reflect the actual situation (mainly due to inaccurate measurement methods; data collection is incomplete or too one-sided; non-standardized self-evaluation and other defects in the data collection process). The second type of subjective structural bias in the process of data collection (such as the purpose of predicting career success rate through subjective patriarchal in the collection of professional data). The former data deviation can be solved by "cleaning the data" or improving the data collection process. But the latter requires complex manual interventions. It is worth noting that although many organizations have done a lot of work to solve this problem, it is still inconclusive as to how to "detect" data deviation. When the collected data has the above deviations, the artificial intelligence system trained by the data may also have corresponding deviations, and the generated models or results that are unwilling to avoid will copy and amplify the deviation. In this case, the decisions made by the artificial intelligence system will have a differential effect, which will lead to social injustice. And this unfairness is more than artificial prejudice and injustice. In industries dominated by risk control, with the widespread use of artificial intelligence systems, the phenomenon of nuances and alienation between people has increased significantly, especially in insurance and other social guarantee industries. The application of artificial intelligence systems enables companies to more effectively identify specific groups and individuals through “reverse selectionâ€, thus effectively avoiding risks. For example, in the field of medical insurance, artificial intelligence systems analyze the characteristics and performance behavior of policyholders, and charge more premiums to those who are identified as special diseases or who have a high incidence in the future. In this case, it is especially disadvantageous for those who are in poor health and have poor financial ability. This is why critics often blame that even if the artificial intelligence system is accurate and the insurer behaves rationally, the effect is often negative. Competition in the insurance industry may exacerbate this trend, and eventually the application of artificial intelligence systems may exacerbate this inequality. Of course, the normative principles of relevant anti-discrimination laws and regulations can help solve these problems, although this method may not be the most effective and fair. In addition, the design and deployment of artificial intelligence systems is also important, but the existing legal framework may hinder the corresponding research. For example, the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) have limited research in this area, so the current regulations need to be reformed to ensure that the necessary research can proceed smoothly. Magnesium Fluoride CAS No. 7783-40-6 Magnesium Fluoride Basic Information Blood Plus Magnesium Fluoride,Fluoride Blocks Magnesium Uptake,Fluoride Reacts With Magnesium,Magnesium Fluoride Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com
Product Name: Magnesium fluoride
CAS: 7783-40-6
MF: F2Mg
MW: 62.3
EINECS: 231-995-1
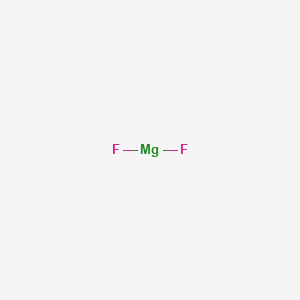
Magnesium Fluoride Chemical Properties
Melting point 1248 °C
Boiling point 2260 °C
Density 3.15 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
Refractive index 1.365
Form random crystals
Color White to off-white
Specific Gravity 3.15
Water Solubility 87 mg/L (18 ºC)